Prototype of a National Mediator Platform for Interoperable Educational Technologies.
Sep. 20, 2021 to Jan. 19, 2022
The Corona pandemic saw a shift of teaching and learning into the digital space. For students and teachers, this presented a number of organizational, technical, and didactic challenges. In particular, the numerous isolated solutions offered by various educational institutions made it difficult for users to take full advantage of digital learning. The National Education Platform, initiated by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), now aims to provide a technical meta-platform based on open standards that creates the foundation for a interconnected, powerful and interoperable teaching-learning infrastructure. The Common Learning Middleware (CLM) developed by Fraunhofer FOKUS was selected by the BMBF as one of three prototypes of the National Education Platform within the framework of the “mEDUator” project.

The Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft and the Fraunhofer Institute FOKUS have been working on a variety of research and development projects related to adaptive, interoperable educational technologies. The most important preliminary work in this context, which also forms the basis for the “mEDUator” project, is the Common Learning Middleware (CLM), which has been implemented in two phases since October 2018. The Common Learning Middleware acts as a mediator for all relevant components of modern learning management and education ecosystems – including user interfaces, authentication systems, user and enrollment management, and various databases for learning media, metadata, and profile and learning data. In addition, various other services can be connected to the interoperable interfaces, for example, for the use of artificial intelligence to evaluate learning activities, the presentation of content in virtual and augmented realities, or the secure verification of educational certificates using blockchain technologies. At the same time, the services do not have to follow the same interoperability standards, as there are definitely alternative offerings for this. Thus, the middleware also serves as a “translator” between alternative specifications (e.g., LTI and cmi5).
mEDUator – Implemented scenarios
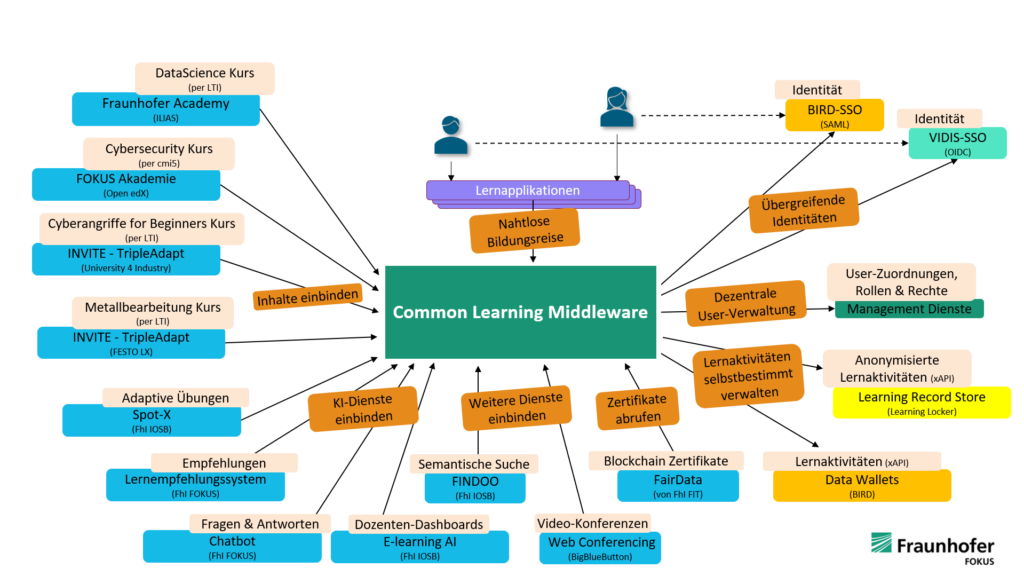
As such, this is the first middleware of its kind and addresses the needs of educational institutions with complex educational ecosystems by facilitating the development of interoperable software architectures for long-lived adaptive learning environments. No later than when there are many applications, content, and service offerings within an infrastructure, a respective direct connection of the applications to the offerings (even based on open specifications) would be difficult to administer and maintain, which has necessitated the introduction of appropriate middleware to orchestrate the services. Instead of a monolith, the mediator platform enables complex microservice infrastructures and the best-of-breed paradigm – where there can be specialized solutions from different providers for every need.
The “mEDUator” project focuses on the provision of the Common Learning Middleware as a prototype of the National Education Platform. This involves the technical provision and operation of the Common Learning Middleware as well as the connection of various offerings from other projects and initiatives. Particular importance is attached to organizational and administrative issues such as data protection and data and IT security.
The piloting of the CLM is funded by the BMBF as part of the “National Education Platform Initiative” and implemented by Fraunhofer FOKUS together with the Fraunhofer Academy. In addition, the project is supported by the following associated partners: German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), FESTO Didactic SE, Mansystems Deutschland GmbH, University4Industry, HTW Berlin, Berliner Hochschule für Technik, TH Brandenburg, HS Albstadt-Sigmaringen, Fraunhofer IOSB and Fraunhofer FIT as well as by the project consortia of the BMBF-funded projects “TripleAdapt” and “EXPAND+ER WB³”.
Gefördert vom Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung. Finanziert von der Europäischen Union – NextGenerationEU.

Funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Financed by the European Union – NextGenerationEU.

